According to a new study, a moon region at the centre of a new worldwide space race due to the possibility of water ice may be less habitable than previously thought.
Interest in the lunar south pole peaked last year when India’s Chandrayaan-3 mission performed the first successful soft landing in the region, just days after Russia’s Luna-25 spacecraft crashed while attempting the same feat. NASA has chosen the region as the landing location for its Artemis III mission, which could send men to the Moon as early as 2026, and China has ambitions to build future habitats there.
However, a NASA-funded study is now raising the alarm: As the Moon’s core gradually cools and shrinks, its surface develops creases, similar to a grape shrivelling into a raisin, resulting in “moonquakes” that can continue for hours and landslides. Much like the rest of the natural satellite’s surface, the area near the south pole that has sparked so much curiosity is prone to seismic disturbances, which could endanger future human residents and equipment.
Earth’s Moon Is Shrinking. Here’s What Scientists Say That Could Mean
“This is not to alarm anyone and certainly not to discourage exploration of that part of the south pole of the moon,” said the study’s lead author, Thomas R. Watters, a senior scientist emeritus in the National Air and Space Museum’s Centre for Earth and Planetary Studies, “but to raise the caution that the moon is not this benign place where nothing is happening.”
Identifying the source of moonquakes
According to researchers, the Moon’s circumference has shrunk by about 150 feet over the previous few million years, a significant amount in geological terms but insufficient to affect Earth or tidal cycles.
However, on the lunar surface, the situation is much different. Despite its appearance, the Moon contains a hot interior that causes seismic activity.
“There is an outer core that’s molten and is cooling off,” Watters told reporters. “As it cools, the moon shrinks, the interior volume changes and the crust has to adjust to that change — it’s a global contraction, to which tidal forces on the Earth also contribute.”
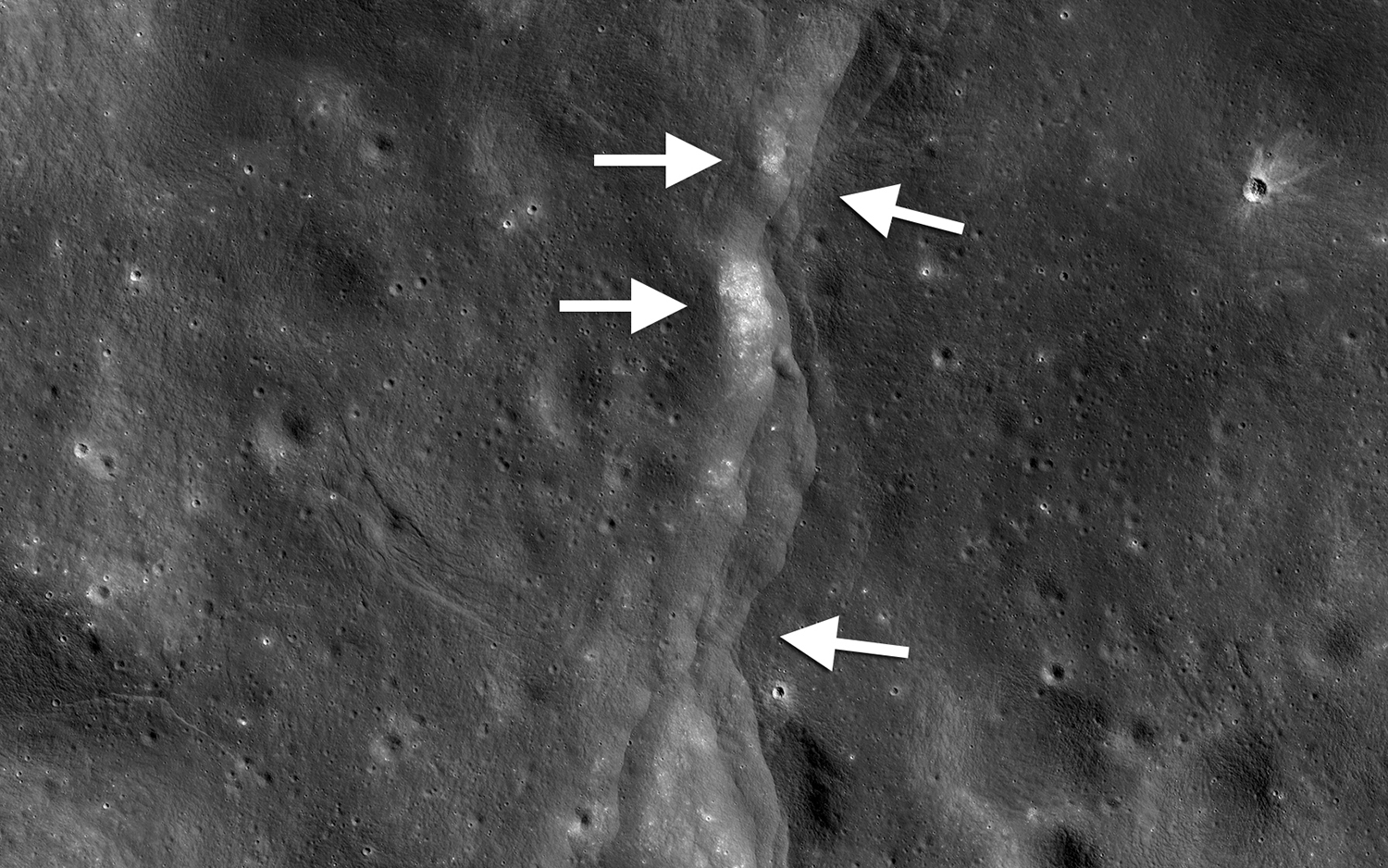
Because the Moon’s surface is brittle, this pushing causes cracks, which geologists call faults. “The moon is thought of as being this geologically dead object where nothing has happened for billions of years, but that couldn’t be more far from the truth,” he said. “These faults are extremely young, and things are happening. We’ve spotted landslides that occurred while the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter was in orbit around the Moon.”
Earth’s Moon Is Shrinking. Here’s What Scientists Say That Could Mean
NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, or LRO, was launched in 2009 and is surveying the Moon’s surface using a variety of instruments. Watters and his colleagues utilised data obtained by LRO to relate a powerful moonquake observed with instruments left by Apollo astronauts more than 50 years ago to a sequence of faults in the lunar south pole.
“We knew from the Apollo seismic experiment, which were four seismometers that operated for a period of about seven years, that there were these shallow moonquakes, but we didn’t really know what the source was,” he said. “We also knew that the greatest of the shallow moonquakes identified by the Apollo seismometers occurred around the south pole. It kind of turned into a detective story to figure out what the cause was, and it turns out that these young flaws are the best suspects.”
The strongest recorded earthquake had a magnitude of 5.0. That would be considered mild on Earth, but Watters believes the Moon’s reduced gravity would make it feel worse.
“Gravity is significantly stronger on Earth, keeping you stuck to the surface. “On the moon, it’s much smaller, so even a small amount of ground acceleration could knock you off your feet if you’re walking,” he explained. “That shaking can start throwing things around in a low G environment.”
Moonquakes: Short-term and long-term implications
According to research coauthor and NASA planetary scientist Renee Weber, the study’s conclusions will not impact the Artemis III landing area selection process because of the mission’s scale and duration.
Earth’s Moon Is Shrinking. Here’s What Scientists Say That Could Mean
“This is because estimating how often a specific region experiences a moonquake is difficult to do accurately, and like earthquakes, we can’t predict moonquakes,” he said. “Strong shallow moonquakes are infrequent and pose a low risk to short-term missions on the lunar surface.”
She said that NASA has identified 13 Artemis III candidate landing areas near the lunar south pole based on characteristics such as the region’s capacity to land safely, the potential to accomplish science objectives, launch window availability, and terrain, communications, and illumination conditions. Two astronauts will live and work on the lunar surface for approximately one week as part of the mission.
However, Weber stated that for long-term human settlement on the Moon, geographic qualities such as proximity to tectonic features and topography could be considered during the site selection.
Like flashlights on the Moon.
Moonquakes could pose a concern for future manned landing missions, according to Yoshio Nakamura, a professor emeritus of geophysics at the University of Texas at Austin and one of the experts who first examined the data acquired by the Apollo seismic stations.
However, Nakamura, who was not part of the study, argues regarding the cause of the quakes, claiming that Apollo data suggests the phenomenon originates tens of kilometres below the surface.
“We still don’t know what causes shallow moonquakes, but it is not the sliding fault near the surface,” he told reporters. “Regardless of what causes those quakes, it is true that they pose a potential threat to future landing missions, and we need more data about them.”
Regardless of the underlying cause, the potential danger moonquakes pose to astronauts will be limited because, at least shortly, humans will only be on the Moon for short periods, a few days at most, according to Allen Husker, a research professor of geophysics at the California Institute of Technology who was not involved in the study.
“It is highly improbable that a major moonquake will occur while they are present. However, it is useful to know that these seismic sources (which cause the quakes) exist. “They can provide an opportunity to better study the moon, just as earthquakes do on Earth,” Husker added. “By the time there is an actual moon base, we should have a much better idea of the actual seismic hazard with upcoming missions.”
Jeffrey Andrews-Hanna, an associate professor of planetary science at the University of Arizona who wasn’t involved in the study, shares that viewpoint. “Moonquakes are an incredible tool for doing science,” he explained in an email. “They’re like headlights in the lunar interior, illuminating the structure for us to see. Studying moonquakes at the South Pole will reveal more about the moon’s internal structure and current activity.
SOURCE – CNN