News
US Senate Votes to Make Daylight Saving Time Permanent in 2023
The US Senate has passed legislation that will make daylight saving time permanent in 2023, abolishing the twice-yearly changing of the clocks in a move backed by advocates who want brighter afternoons and more economic activity.
The Sunshine Protection Act was approved overwhelmingly by voice vote in the US Senate.
The bill must now be passed by Congress, which will hold a committee hearing before the daylight saving time bill can be signed into law.
According to Reuters, a House Speaker spokesperson Nancy Pelosi declined to say if she supports the bill but was attentively analyzing it.
After discussion, Florida Senator Marco Rubio, a daylight saving time bill’s sponsor, stated that the change would not take effect until November 2023.
“I know this isn’t the most pressing issue affecting America, but it’s one of those matters on which we can all agree,” Rubio added. “If we can pass this, we won’t have to do this stupidity any longer.”
“Pardon the pun,” he continued, “but this is an idea whose time has come.”
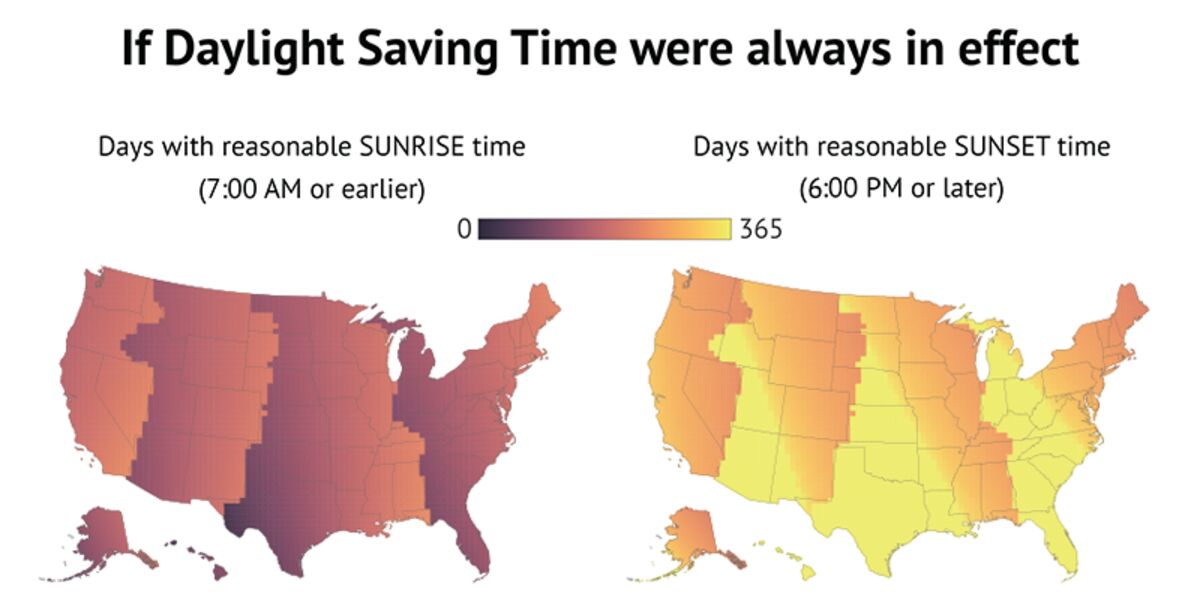
Resumption of daylight saving time
The National Association of Convenience Stores is opposed to the shift, warning Congress last month that “kids should not be going to school in the dark.”
Most of the United States resumed daylight saving time on Sunday, moving ahead one hour. In November, the United States will revert to standard time.
Since 2015, over 30 states have submitted legislation to abolish daylight saving time.
The House Energy and Commerce Committee convened a hearing last week, and the committee’s chairman, Representative Frank Pallone, stated, “The loss of just one hour of sleep appears to affect us for several days thereafter. It can also disrupt the sleeping routines of our children and pets.”
Pallone supports the elimination of clock-switching but has not decided whether daylight or standard time should be the permanent decision.
Beth Malow, head of the Vanderbilt Sleep Division, testified at the hearing that daylight savings time makes it more difficult to remain attentive in the morning, claiming it’s “like living in the incorrect time zone for almost eight months out of the year.”
Americans prefer not to change their Clocks
Pallone referenced a 2019 poll in which 71% of Americans said they would prefer not to change their clocks twice a year.
Supporters argue that the change could prevent a modest rise in car accidents that occurs around time changes, and they refer to studies that show a small increase in the rate of heart attacks and strokes shortly after the time shift.
They say that the policy might benefit businesses such as golf courses, which would benefit from increased evening daylight.
“It has substantial ramifications for our economy and daily life,” Senator Ed Markey, another key sponsor, stated.
After being tested in 1918, daylight saving time has been used in practically all of the United States since the 1960s. Year-round daylight savings time was utilized during WWII, and it was reinstated in 1973 to minimize energy consumption due to an oil embargo, only to be removed a year later.
The bill would allow Arizona and Hawaii, which do not observe daylight saving time, as well as American Samoa, Guam, the Northern Mariana Islands, Puerto Rico, and the United States Virgin Islands, to continue on standard time.
According to advocates, the shift would allow youngsters to play outside later and minimize seasonal depression.